Spherical CNNs on Unstructured Grids
Chiyu "Max" Jiang Jingwei Huang Karthik KashinathPrabhat Philip Marcus Matthias Niessner
[Paper] [Code] [Bibtex]
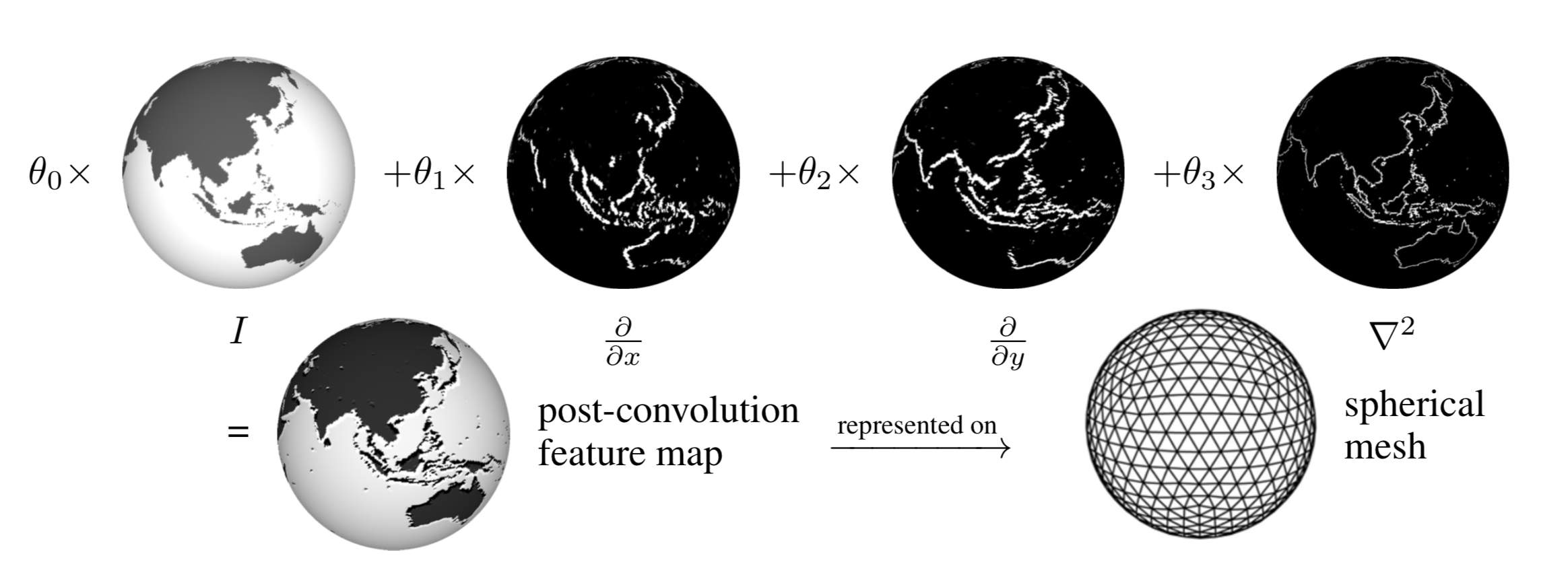
Figure 1 Illustration for the MeshConv operator using parameterized differential operators to replace conventional learnable convolutional kernels.
Abstract
We present an efficient convolution kernel for Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) on unstructured grids using parameterized differential operators while focusing on spherical signals such as panorama images or planetary signals. To this end, we replace conventional convolution kernels with linear combinations of differential operators that are weighted by learnable parameters. Differential operators can be efficiently estimated on unstructured grids using one-ring neighbors, and learnable parameters can be optimized through standard back-propagation. As a result, we obtain extremely efficient neural networks that match or outperform state-of-the-art network architectures in terms of performance but with a significantly lower number of network parameters. We evaluate our algorithm in an extensive series of experiments on a variety of computer vision and climate science tasks, including shape classification, climate pattern segmentation, and omnidirectional image semantic segmentation. Overall, we present (1) a novel CNN approach on unstructured grids using parameterized differential operators for spherical signals, and (2) we show that our unique kernel parameterization allows our model to achieve the same or higher accuracy with significantly fewer network parameters.
Gallery

Figure 2 Visualization of semantic segmentation results on test set. Our results are generated on a level-5 spherical mesh and mapped to the equirectangular grid for visualization. Model underper- forms in complex environments, and fails to predict ceiling lights due to incomplete RGB inputs.